By 2025, large language models (LLMs) aren’t just experiments anymore-they’re running core business processes in companies across finance, healthcare, retail, and manufacturing. The shift from pilot projects to production-grade systems has been rapid. Organizations aren’t asking if they should use LLMs anymore. They’re asking which use cases deliver the most value, and how to deploy them without breaking compliance, security, or budgets.
Customer Service That Actually Understands You
Gone are the days of scripted chatbots that loop you back to the same menu. In 2025, enterprise customer service is powered by Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). This means LLMs don’t guess answers-they pull from your company’s internal documents, policies, and past interactions to give accurate, context-aware responses. A global retail chain saw customer satisfaction scores jump 24 points after switching to a RAG-powered support system. Their AI could answer questions like, "What’s my refund policy if I bought this item during Black Friday?" by pulling from real policy documents, warranty terms, and regional legal rules-all in under two seconds. Accuracy hit 91%, up from 62% with older rule-based systems. The secret? It’s not the model size. It’s the knowledge base. Companies that succeed here spend months cleaning up their internal wikis, support tickets, and product manuals before even touching an LLM. Without good data, even the best model fails.Automating Document Review and Compliance
Legal teams used to spend weeks sifting through contracts, NDAs, and regulatory filings. Now, they hand those documents to LLMs and get summaries, risk flags, and compliance checks in minutes. A Fortune 500 bank automated contract review for loan agreements using a fine-tuned LLM. The system scanned 12,000 contracts in two weeks-something that would’ve taken 18 months manually. It flagged 37% more risky clauses than the human team had caught in the previous year. The model was trained on past legal disputes and regulatory violations, so it learned what to watch for: hidden termination clauses, non-compliant interest rate structures, jurisdiction conflicts. Healthcare providers use similar systems to review patient records for HIPAA compliance. LLMs scan for exposed Social Security numbers, unauthorized disclosures, or missing consent forms. One hospital reduced compliance violations by 68% in six months after deploying this system. The catch? These models need to be fine-tuned on your company’s specific terminology. A legal LLM trained on tech contracts won’t understand medical billing codes. Domain-specific tuning isn’t optional-it’s the difference between a helpful tool and a dangerous liability.Fraud Detection That Learns Like a Human
Traditional fraud systems rely on rigid rules: "If transaction > $10,000 and overseas, flag it." But fraudsters adapt. They break rules in new ways every day. Enterprises now use LLMs to detect anomalies in patterns-not just numbers. A JPMorgan Chase team built a fraud detection system using a fine-tuned Llama 3 model. Instead of looking for known fraud patterns, the AI analyzed millions of transactions and learned what "normal" looked like for each customer: typical spending times, merchant categories, device usage, even typing speed on mobile apps. The result? 94.7% detection accuracy and 38% fewer false positives. That means fewer angry customers getting blocked during legitimate purchases. The system also reduced investigation time by 70%. Instead of manual reviews, analysts get AI-generated summaries: "This transaction matches the user’s travel history, but the IP is from a known proxy server-investigate further."
Accelerating Employee Onboarding and Training
New hires used to spend weeks buried in PDFs, waiting for meetings, and asking the same questions over and over. Now, they get an AI coach. A multinational consulting firm rolled out an internal LLM that answers questions like, "How do I submit my expense report?" or "What’s the process for escalating a client complaint?" It pulls from internal wikis, HR manuals, and past Slack conversations. New employees get instant answers-no manager needed. Results? Onboarding time dropped from 4 weeks to 10 days. Employee satisfaction scores rose 22%. And managers got back 12 hours a week they used to spend answering basic questions. This works best when the LLM is trained on real internal content-not generic templates. The model needs to understand your company’s jargon, approval workflows, and even cultural norms. One company found their AI kept saying "contact your manager" when the real process was to email a specific Slack channel. They fixed it by feeding the model 3,000 real Slack threads.Turning Unstructured Data Into Actionable Insights
Most business data isn’t in spreadsheets. It’s in emails, call transcripts, support chats, customer reviews, and meeting notes. That’s 80-90% of enterprise data-and it’s useless without structure. An e-commerce company used an LLM to analyze 500,000 customer reviews. The AI didn’t just count positive and negative words. It grouped feedback by product feature: "battery life too short," "app crashes when scanning barcode," "customer service took 4 days to reply." Then it ranked them by frequency and emotional intensity. Product teams got a live dashboard showing which issues were trending. Within two weeks, they fixed the app crash bug. Sales teams used the insights to retrain reps on how to handle battery complaints. Revenue from that product line rose 11% in the next quarter. This isn’t sentiment analysis. It’s deep semantic understanding. The model identifies not just what people said, but what they meant-and what they didn’t say.Code Generation That Actually Ships
LLMs aren’t just for writing emails. They’re writing code. At a fintech startup, developers now use LLMs to generate API endpoints, SQL queries, and unit tests. The AI doesn’t replace engineers-it handles boilerplate. One team reduced time spent on repetitive code tasks by 60%. They focused on architecture and edge cases; the AI handled the rest. But here’s the key: they didn’t trust the AI blindly. Every line of code generated by the model was reviewed by a human. The LLM was trained on their internal codebase, so it learned their style, naming conventions, and security standards. This use case is growing fast. Code generation now accounts for 28% of all enterprise LLM deployments, according to MenloVC. The most successful teams treat AI as a pair programmer-not a replacement.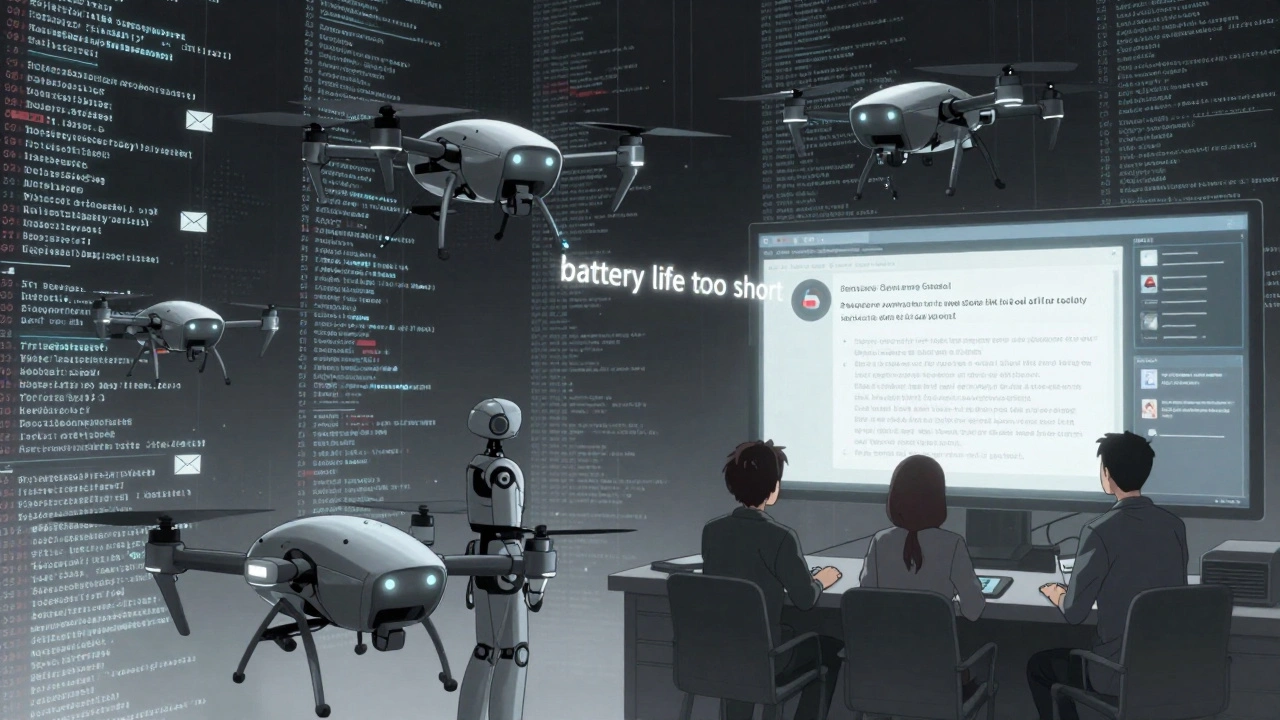
What’s Working-and What’s Not
The companies winning with LLMs in 2025 aren’t the ones with the biggest budgets. They’re the ones who understand three things:- Accuracy matters more than speed. A model that’s 92% accurate on your data beats one that’s 98% accurate on generic text.
- Security isn’t optional. 94% of financial and healthcare firms require on-premise or private cloud deployment. Public APIs with sensitive data? That’s a lawsuit waiting to happen.
- Start small, then scale. Don’t try to automate everything at once. Pick one high-impact, well-defined task-like reviewing contracts or answering FAQs-and nail it before moving on.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Business
The market has narrowed. In 2025, five players dominate enterprise adoption:- Anthropic leads with 38% market share, thanks to strong reasoning and security features. Their Claude Enterprise 3.5 supports 512K tokens and is used by 37% of Fortune 500 companies.
- OpenAI holds 29%, popular for its API reliability and broad tooling.
- Google at 22%, strongest in integration with Workspace and internal enterprise systems.
- Cohere at 7%, favored for multilingual support and low-latency responses.
- Small Language Models (SLMs) like Mistral 7B and IBM’s Granite are growing fast-41% of new deployments now use them.
- Can it connect to your CRM, ERP, and helpdesk systems? (89% of enterprises require this)
- Does it have SOC 2 Type II or HIPAA compliance? (78% require this)
- Can you fine-tune it on your own data? (79% say yes)
- Do you get 24/7 support with a guaranteed SLA? (92% uptime for paid models vs. 85% for open-source)
What’s Next in 2026 and Beyond
The next wave isn’t bigger models. It’s smarter ones. - Industry-specific models are rising fast. Expect LLMs trained only on healthcare data, financial regulations, or manufacturing logs. - Real-time collaboration features will let teams co-edit documents with AI suggestions popping up as they type. - Automated compliance will become standard. LLMs will auto-redact PII, flag GDPR violations, and generate audit trails without human input. Gartner predicts enterprise LLM spending will hit $22.3 billion by 2027. But the winners won’t be the ones with the flashiest demos. They’ll be the ones who built systems that work-quietly, reliably, and securely-day after day.Are large language models safe for enterprise use in 2025?
Yes-but only if deployed correctly. Leading enterprise LLMs now offer on-premise deployment, end-to-end encryption, and SOC 2 Type II or HIPAA compliance. 94% of financial and healthcare firms require these features. The risk isn’t the model itself-it’s using public APIs with sensitive data or skipping data governance. Companies that treat LLMs like any other enterprise software-securing data, auditing outputs, and enforcing access controls-see minimal risk.
Do I need a data science team to use LLMs in my company?
Not necessarily. While fine-tuning models or building custom RAG systems requires AI expertise, many enterprise platforms now offer no-code or low-code interfaces. Business analysts can deploy basic chatbots or document summarizers after 2-3 weeks of training. The real bottleneck is data preparation-not the AI. Cleaning up your internal documents, tagging knowledge bases, and structuring your data takes longer than choosing a model.
What’s the biggest mistake companies make with LLMs?
Skipping data preparation. 78% of failed LLM projects trace back to poor-quality or unstructured training data. An LLM can’t magically understand your business if it’s fed messy emails, outdated wikis, and incomplete manuals. Successful deployments spend 3-6 months curating data before even training a model. Quality data beats model size every time.
Are open-source LLMs a good choice for enterprises?
For experimentation, yes. For production, rarely. Open-source models like Llama 4 dropped from 19% to 13% of enterprise workloads in 2025. They lack enterprise-grade support, 24/7 SLAs, compliance certifications, and consistent uptime. While they offer customization and avoid vendor lock-in, most companies can’t afford the risk of downtime or compliance failures. Paid solutions deliver 92% uptime vs. 85% for open-source-and that gap matters in critical systems.
How do I measure ROI from an LLM implementation?
Track specific metrics tied to your use case. For customer service: reduce ticket volume, increase CSAT scores, lower agent handling time. For document review: cut review time, reduce compliance violations, lower legal costs. For code generation: reduce developer hours spent on boilerplate. McKinsey recommends tracking 12-15 KPIs per deployment. Don’t just measure speed-measure accuracy, user satisfaction, and error reduction. The goal isn’t automation. It’s better outcomes.

Jitendra Singh
Really solid breakdown. I've seen teams skip data prep and wonder why the model keeps giving weird answers. It's not magic-it's garbage in, garbage out. Took us 5 months just to clean up our internal wikis before we even trained anything. Worth it though.
Madhuri Pujari
Of course it works-when you have a billion-dollar budget and a team of 20 data scientists. Meanwhile, small companies are stuck with half-baked RAG systems that hallucinate refund policies because someone forgot to update the FAQ PDF in 2022. This isn't innovation-it's elitist tech theater.
Sandeepan Gupta
Madhuri, you're missing the point. The issue isn't budget-it's discipline. Clean data isn't a luxury, it's the foundation. I've helped three mid-sized firms deploy LLMs with under $50k and zero data scientists. They just stopped ignoring their internal docs and started organizing them. That’s all.
Tarun nahata
THIS. RIGHT HERE. The moment I saw that hospital cut compliance violations by 68%? I nearly jumped out of my chair. This isn't just tech-it's saving lives. Imagine a nurse not having to worry about a patient's SSN being exposed because the AI caught it before it went out. That’s the kind of win that keeps me up at night-in a good way.
Aryan Jain
They're lying. LLMs are being used to manipulate customer sentiment. That '94.7% detection accuracy'? It's just training the AI to ignore red flags so corporations don't get caught. And the 'on-premise' thing? A distraction. They're still sending data to the cloud-just through a backdoor. You think the government doesn't have access to these models? Wake up.
Agni Saucedo Medel
Love how this post focuses on real impact, not hype. Also, the part about SLMs? Huge. We switched to Mistral 7B and our monthly cloud bill dropped by 60%. Still works great for our use case. 🙌
ANAND BHUSHAN
Yeah, the code generation part is legit. We use it for boilerplate SQL and unit tests. Saves hours. But I still read every line. No way I'm letting AI write production code without a second look.
Diwakar Pandey
One thing people overlook: the human cost. When you automate answering basic onboarding questions, managers get their time back-but new hires lose the chance to build relationships. I’ve seen teams become isolated because the AI became the first point of contact. Sometimes, the slow way is the right way.
Geet Ramchandani
Let’s be real-this whole thing is just corporate fluff dressed up as innovation. You say 'accuracy matters more than speed'? That’s what they all say before they deploy a model that gets sued for misclassifying a patient’s diagnosis. And don’t even get me started on the 'no-code' nonsense. If you can’t explain how your model works, you shouldn’t be using it. 78% of failures are due to bad data? That’s not a statistic-it’s a confession of negligence.
Pooja Kalra
Interesting how everyone talks about data-but no one asks why the data was messy in the first place. Who allowed those wikis to rot? Who let the Slack threads become a graveyard of half-answers? The real problem isn’t the AI-it’s the organizational rot that made the AI necessary in the first place. We’re automating symptoms, not curing disease.