When your large language model starts giving wrong answers, slowing down, or costing more than expected, you don’t want to find out from a customer complaint. You need to know before it happens. That’s where LLM health monitoring comes in-not as a nice-to-have, but as a core part of running AI in production.
Most teams start by tracking accuracy. But that’s like only checking if your car’s engine is on. What if it’s running hot? What if it’s using too much fuel? What if it’s giving the wrong directions even when the engine is fine? LLMs are the same. You need a full dashboard that shows you how the model is performing across technical, business, and ethical dimensions.
What Really Matters in LLM Health?
Forget generic metrics like ‘accuracy.’ That’s too vague for generative models. Instead, focus on these five measurable dimensions:
- Model quality: Are the responses factually correct? How often does it make up facts (hallucinations)? Is the output coherent and fluent?
- Operational efficiency: How fast does it respond? How many requests can it handle per second? Are your GPUs or TPUs being used efficiently?
- Cost management: How much does each response cost in tokens? Is spending going up without a corresponding improvement in quality?
- User engagement: Are people finishing their interactions? Are they coming back? Are they rating responses positively?
- Safety and compliance: Does it generate harmful, biased, or non-compliant content? Is there a full audit trail for regulated industries?
These aren’t theoretical. In healthcare, a hallucination rate above 5% in diagnostic suggestions can lead to real patient harm. In finance, missing an audit trail for a loan recommendation could trigger regulatory fines. These aren’t just tech issues-they’re business risks.
Key KPIs You Must Track
Here’s what actual teams are measuring in production:
| Category | KPI | How It’s Measured | Acceptable Threshold |
|---|---|---|---|
| Model Quality | Hallucination Rate | Percentage of responses containing false claims not in source data | < 5% |
| Model Quality | Groundedness | Percentage of claims supported by provided context | > 85% |
| Model Quality | Coherence | Human-rated 1-5 scale on logical flow and clarity | Average ≥ 4.0 |
| Operational | Latency (first token) | Milliseconds from request to first output token | < 1,500ms |
| Operational | Throughput | Requests per second | Based on SLA (e.g., 50+ RPS) |
| Cost | Cost per 1,000 tokens | USD spent per 1,000 tokens processed | Down 10% YoY |
| Safety | Harmful Content Rate | Percentage flagged by safety filters or human review | < 0.1% |
| Engagement | User Completion Rate | Percentage of users who finish their query session | > 75% |
These numbers aren’t random. A 2024 study by Codiste found that enterprises with hallucination rates below 5% saw a 7.2% increase in customer satisfaction scores. That’s not a coincidence-it’s a direct link between technical health and business value.
How Dashboards Turn Data Into Action
A dashboard isn’t just a pretty chart. It’s your early warning system. The best ones show you three things:
- What’s broken: Real-time spikes in latency, cost, or hallucination rates.
- Why it’s broken: Correlation with recent model updates, data drift, or traffic spikes.
- What to do: Automated alerts tied to specific actions-like rolling back a model or triggering a human review.
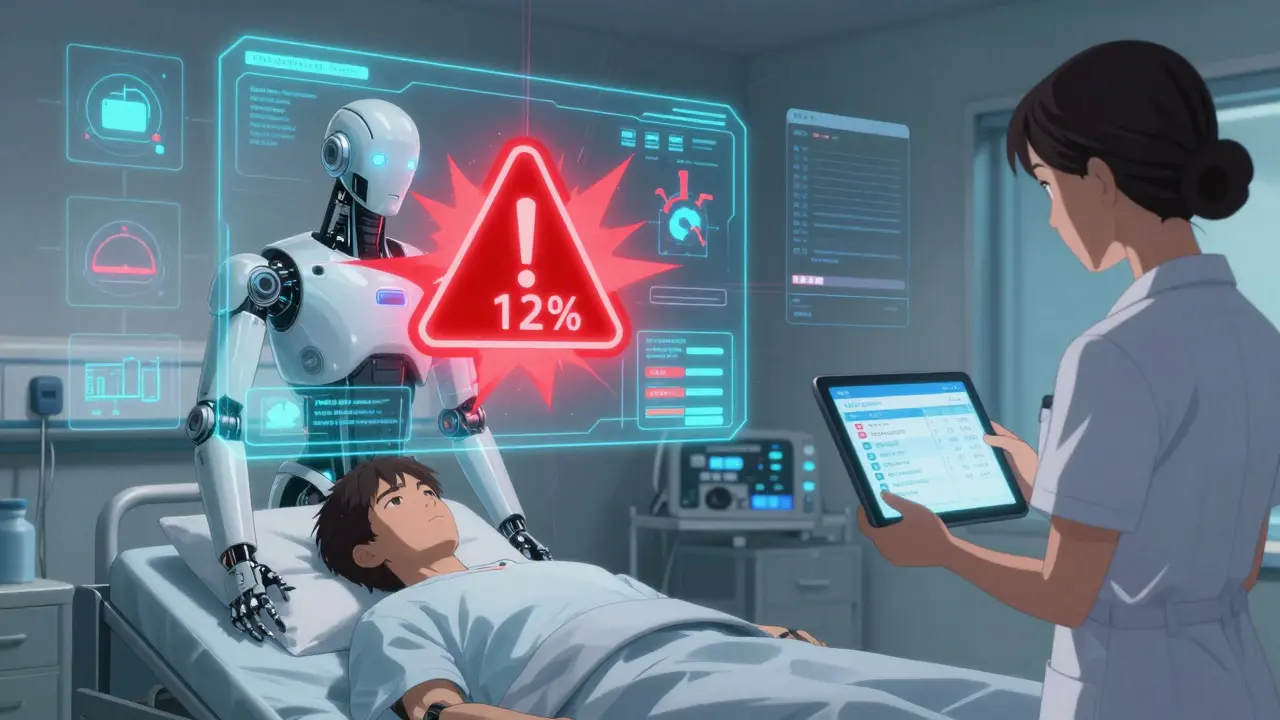
For example, one hospital system using Google Cloud’s Vertex AI Monitoring saw a sudden 12% spike in hallucination rates. The dashboard showed the spike happened right after a model update. They rolled back within 30 minutes-before any patient records were affected. That’s the power of a good dashboard.
Don’t just monitor system metrics like CPU usage. That’s like checking your car’s oil level while ignoring the check-engine light. You need to monitor what matters to users: response quality, speed, and safety.

Industry-Specific Needs
Not all LLMs are the same. What works for a customer support bot won’t work for a medical diagnosis tool.
In healthcare, teams track:
- Diagnostic accuracy against gold-standard medical records
- Bias detection across age, gender, and race groups
- Compliance with HIPAA and audit trail completeness
Censinet found healthcare systems use 22% more data validation checks than general-purpose models. Why? Because one wrong suggestion can cost a life.
In finance, focus shifts to:
- Explainability: Can you justify why the model recommended a loan denial?
- Regulatory adherence: Does every output comply with anti-discrimination laws?
- Traceability: Can you reconstruct every decision for auditors?
MIT Sloan documented a cardiac risk prediction model in Sweden that didn’t just flag high-risk patients-it became a KPI for cardiologists. If the model’s predictions didn’t match actual patient outcomes over time, the team had to retrain. That’s KPIs driving clinical decisions.
Common Mistakes (And How to Avoid Them)
Most teams fail in three ways:
- Monitoring only technical metrics: Tracking latency and throughput without linking them to user satisfaction. AWS found organizations that do this see 22% lower user completion rates.
- No ground truth: You can’t measure hallucinations if you don’t know what the right answer is. Teams need 3-5 human reviewers per 100 samples to get reliable data.
- Alert fatigue: Too many alerts with no clear thresholds. One Reddit user said they got 47 alerts in a single day-none of which were urgent. Set severity levels: low, medium, high. Only escalate high.
Fix this by defining KPIs with risk impact. For example: “A 15% increase in latency beyond 2,000ms triggers a high-severity alert because user drop-off increases by 22%.” That’s actionable.

Cost and Complexity
Yes, monitoring adds overhead. Comprehensive tracking can increase infrastructure costs by 12-18%, according to XenonStack. But here’s the math: if your model costs $50,000/month to run and a 10% drop in quality leads to a $200,000 loss in customer trust, monitoring is cheap.
Start small. Pick one high-risk use case-a customer service bot, a medical triage tool, or a compliance checker. Build your dashboard around it. Use open-source tools like Prometheus and Grafana to start. Then scale.
Enterprise teams with legacy systems take 8-12 weeks to get monitoring live. Startups with ML engineers can do it in 2-4 weeks. The difference isn’t tech-it’s clarity of goals.
What’s Next? Predictive Monitoring
The next wave isn’t just watching what’s happening-it’s predicting what will happen.
Google Cloud’s October 2024 update lets you forecast how a 10% change in hallucination rate will affect customer satisfaction. Coralogix’s new tool flags diagnostic inaccuracies when LLM outputs deviate more than 5% from medical guidelines. And by 2026, 80% of enterprise systems will use causal AI to find root causes-not just detect anomalies.
Right now, only 32% of organizations use consistent metrics across projects. That’s a problem. If you can’t compare your healthcare model to your finance model, you can’t learn from each other.
The goal isn’t perfect models. It’s healthy ones. Ones you can trust, scale, and fix before they break.
What’s the difference between LLM monitoring and traditional ML monitoring?
Traditional ML models predict fixed outputs-like whether an email is spam or a loan will default. Their performance is measured with precision, recall, and F1 scores. LLMs generate open-ended text, so those metrics don’t apply. Instead, you need to measure hallucinations, coherence, groundedness, and safety-things that aren’t binary. LLM monitoring also tracks cost per token and latency in real time, which is less critical for static models.
How often should I review my LLM KPIs?
Review them weekly during early deployment. Once stable, monthly reviews are enough-but only if you have automated alerts for critical issues. Change your KPIs whenever your use case changes. For example, if you add a new language support, you need new fluency metrics. If you move from customer service to medical triage, safety and compliance metrics must become top priorities.
Can I use open-source tools for LLM monitoring?
Yes, but with limits. Tools like Prometheus, Grafana, and LangSmith work well for basic tracking-latency, throughput, cost. But they don’t automatically measure hallucinations or groundedness. You’ll need to build custom evaluators or integrate with human review systems. For regulated industries, commercial tools like Arize, WhyLabs, or Google Cloud’s Vertex AI offer pre-built compliance and bias detection features you can’t easily replicate.
How do I know if my LLM is getting worse over time?
Track trends, not just snapshots. If your hallucination rate climbs from 3% to 6% over three weeks, that’s a problem-even if it’s still under 10%. Look for drift in user feedback scores, rising latency without traffic increase, or cost per token going up while quality stays flat. These are signs your model is degrading. Use statistical process control charts to spot these trends early.
Do I need a dedicated team for LLM monitoring?
Not necessarily a full team, but you need someone accountable. In startups, that’s often the ML engineer. In enterprises, it’s a ModelOps or AI Governance role. The person doesn’t need to be a data scientist-they need to understand the business impact of each KPI. If a 10% drop in user satisfaction means $1M in lost revenue, they need to know that and act on it.
What’s the biggest ROI from LLM monitoring?
The biggest ROI isn’t cost savings-it’s trust. A healthcare provider using LLM monitoring reduced compliance violations by 40% and cut audit prep time from 72 hours to under 2. A financial services firm avoided a $3M regulatory fine by catching a biased loan recommendation before launch. These aren’t hypotheticals. They’re real outcomes from teams that monitored before it was too late.
Next Steps: Where to Start
Don’t try to monitor everything at once. Pick one high-impact use case. Define three KPIs: one for quality, one for cost, one for safety. Build a simple dashboard with real-time alerts. Get human reviewers to validate outputs weekly. Track how changes in the model affect user behavior. After 30 days, you’ll know what works. Then expand.
LLMs aren’t magic. They’re machines. And machines break. The difference between a successful AI project and a failed one isn’t the model-it’s whether you’re watching it closely enough.
kelvin kind
Just started monitoring our support bot with Grafana and Prometheus. Biggest win? Catching a 200ms latency spike that was killing user completion rates. Fixed it before anyone complained.
lucia burton
Let me tell you, if you're not tracking groundedness and hallucination rate in tandem with cost per token, you're flying blind. We saw a 14% drop in customer satisfaction when our hallucination rate crept above 5.2%-even though latency was fine and throughput was optimal. The business doesn't care if your GPU utilization is 87%. They care if the model is lying to their customers. That’s why we built a custom evaluator using LangChain and human-in-the-loop validation. Now we auto-trigger retraining when groundedness dips below 82% for more than 48 hours. It’s not perfect, but it’s way better than reacting to angry emails.
Denise Young
Oh wow, so we’re pretending that ‘coherence’ on a 1-5 human scale is somehow objective? Let’s be real-human raters disagree on whether a response is ‘coherent’ more often than they agree. And yet here we are, treating it like a KPI with a hard threshold of 4.0. Meanwhile, the model is generating perfectly grammatical nonsense that sounds plausible but is factually hollow. You can’t quantify ‘trust’ with a scale. You can only observe it through behavior-like whether users come back. Which, by the way, is the only metric that actually matters. The rest? Just noise dressed up as science.
Sam Rittenhouse
I’ve been on the other side of this-where the model was flagged for ‘harmful content’ because it used the word ‘disabled’ in a medical context. The safety filter didn’t know the difference between clinical terminology and slurs. We had to manually label 2,000 samples to train a custom classifier. It took weeks. But now? Our false positive rate dropped from 18% to 1.3%. The point isn’t to eliminate all risk-it’s to reduce it to a level where you can sleep at night. And yes, that means building your own tools. No vendor solution will ever understand your domain as well as your team does.
Peter Reynolds
Started with one KPI-cost per 1000 tokens. Then added latency. Then user completion. Now we have alerts for all three. We didn’t need a team. Just one person checking the dashboard every morning. The rest? Automated. The dashboard isn’t the point. The action is. If you’re not doing something when the alert fires, you’re just collecting data for a PowerPoint.
Fred Edwords
Actually, the acceptable threshold for hallucination rate should be less than 3%, not 5%. The cited Codiste study showed a 7.2% increase in satisfaction at under 5%, but that’s still 1 in 20 responses being factually incorrect. In high-stakes domains like healthcare, even a 1% hallucination rate is unacceptable. Furthermore, the term ‘groundedness’ is often misused-it should be defined as the proportion of claims that are verifiably supported by context, not merely ‘supported.’ There’s a difference between plausibility and truth. And if you’re not using a gold-standard dataset with annotated ground truth, your metrics are meaningless. Please, for the love of all that is logical, stop using vague terminology in production systems.
Sarah McWhirter
Let’s be honest-this whole LLM monitoring thing is just corporate theater. They’re scared of AI, so they build dashboards to feel in control. But here’s the real truth: every single ‘hallucination’ you’re measuring? It’s just the model being creative. And every ‘bias’? It’s just reflecting the world. You want to fix the model? Fix the data. Fix the training. Fix the people who labeled it. Stop pretending you can monitor your way out of a fundamentally broken system. The model isn’t broken-you are. And your KPIs? They’re just mirrors. And you don’t like what you see.
Ananya Sharma
You think this is about health? It’s about control. You’re not monitoring for safety-you’re monitoring to avoid liability. In healthcare, they don’t care if the model hallucinates-they care if the doctor gets sued. In finance, they don’t care if the model is biased-they care if the regulator fines them. This whole framework is a legal shield wrapped in jargon. And the worst part? You’re all pretending that metrics like ‘user completion rate’ mean anything when users are trapped in a system they can’t escape. If they’re finishing sessions, it’s because they’ve given up. Not because they’re satisfied. You’re measuring compliance, not care. And you call that progress?
Ian Cassidy
Used to track everything. Now I just watch cost and user drop-off. If cost spikes and drop-off spikes? Time to check the model. If cost drops and drop-off drops? Probably fixed something. Simple. Works.
Zach Beggs
One thing I’ve learned: if your dashboard doesn’t have a ‘what changed?’ button, it’s useless. We added a model version diff tool that shows you exactly which prompt template or fine-tune caused the spike. Saved us hours every time. Also, don’t ignore the negative feedback. People don’t rate bad responses-they just leave. That’s your signal.